Methods and Theory : Unsupervised Joint Alignment and Clustering
Overview
Joint alignment of a collection of functions is the process of
independently transforming the functions so that they appear more
similar to each other. Here, functions can be binary, grayscale or
color images, 1D or multidimensional curves, or even 3D scans. The
alignment process is helpful for many scenarios, ranging from a
pre-processing step to clean up a data set to learning the set
of transformations that generate a data set.
Typically, such unsupervised alignment
algorithms fail when presented with complex data sets arising from
multiple modalities or make restrictive assumptions about the form of
the functions or transformations, limiting their generality.
We developed a nonparametric Bayesian model that can automatically
align and cluster a data set. The clustering component can
explicitly handle the multi-modality of complex data sets. Our model
learns the number of clusters in a data-driven fashion and is applicable
to a wide range of function types (e.g. images and curves) and any
transformation function.
Sample Results
Given 100 unlabeled images (top), without any other information, our model chooses to represent the data with two clusters, aligns the images and clusters them as shown (bottom). On this data set, our models clustering accuracy is 94%, compared to 54% with K-means using two clusters.Input: 100 unaligned, unlabelled images

Output: 2 clusters, with each image aligned to its cluster


In our paper, we also present state-of-the-art results on a full 10-digit data set, where 12 clusters were discovered resulting in a clustering accuracy of 87%.
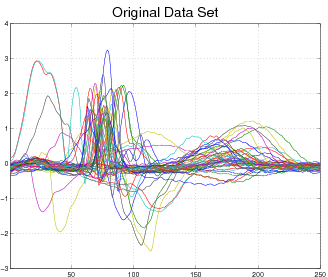
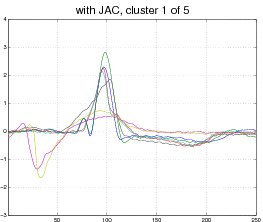
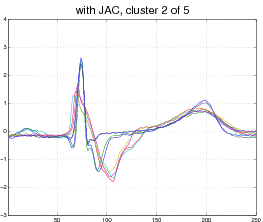
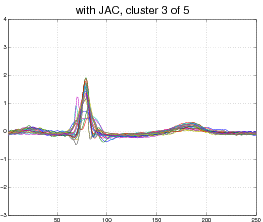
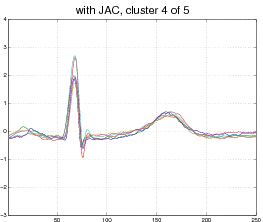
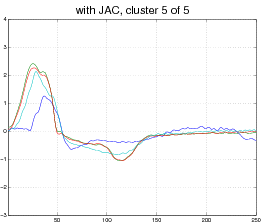
Our model is not limited to affine transformations or even images. Consider, for example, the following data set of EKG heart data (top). Each curve represent a normal or abnormal heart beat, although the data set does not visually cluster into two groups only. In this case our model discovers 5 appropriate clusters and aligns each curve to its cluster (bottom).
Input: EKG curves representing normal and abnormal heart beats
Output: 5 clusters, with each curve aligned to its cluster
Faculty
Graduate Students
Publications
- Marwan Mattar, Allen Hanson, and Erik Learned-Miller
Unsupervised Joint Alignment and Clustering using Bayesian Nonparametrics.
Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence (UAI), 2012.
[pdf]
